Chronic kidney disease management – Things to know
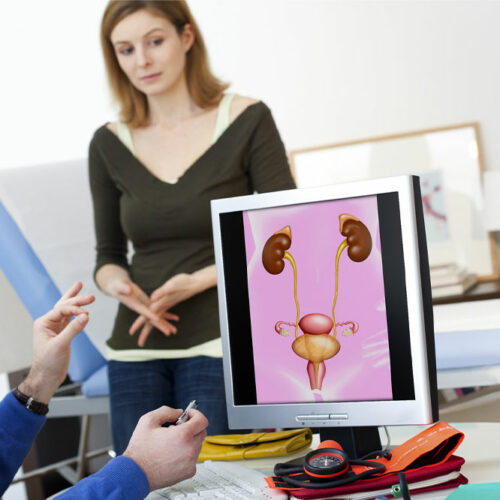
The kidneys in the human body filter all the blood in about 30 minutes to remove wastes, excess fluid, and toxins. The organ also helps control blood pressure, boost red blood cell production, and keep the bones healthy. But an individual may develop chronic kidney disease (chronic kidney failure) – the gradual loss of kidney function. It will hamper the overall functionality of the organ and lead to severe health complications. Symptoms The indicators of chronic kidney disease develop over time if the damage occurs gradually. Losing kidney function may result in an alarming build-up of fluid, body waste, or electrolytes. The signs and symptoms of the condition may also be caused by other health conditions, making kidney disease difficult to diagnose. Moreover, since kidneys cannot recover from lost function, the individual may not develop symptoms until the disease reaches advanced stages. Based on the severity of the disease, a person who suffers from loss of kidney function may experience vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite, chest pain (if there is fluid build-up around the lining of the heart), weakness, fatigue, excessive or poor urination, sleeping difficulties, muscle cramps, itchy or dry skin, hypertension (high blood pressure) that is difficult to manage, shortness of breath (if there is a build-up of fluids in the lungs), swollen feet or ankles, and declined mental sharpness. Causes Chronic kidney disease occurs when a health condition affects the kidney’s function. It leads to kidney damage becoming worse over months and sometimes years. Based on research, the most common health complications that may cause chronic kidney disease include – Type 1 or type 2 diabetes Pyelonephritis, which are recurring kidney infection Glomerulonephritis – an inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units Inflammation of the kidney’s tubules and covering structures (interstitial nephritis) High blood pressure Vesicoureteral reflux – a condition that causes urine to back up into your kidneys Polycystic kidney disease Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract due to health conditions like kidney stones, an enlarged prostate, or certain cancers Other inherited kidney diseases Risk factors Individuals may also risk developing chronic kidney disease due to other influencing factors.
Read More